2 FACTOR AUTHENTICATION
Welcome to the blog of 2FA
MULTI-FACTOR AUTHENTICATION
How multi-factor authentication improves cybersecurity, July 16, 2021
Computer security, cybersecurity or information technology security is the protection of computer systems and networks from information disclosure, theft of or damage to their hardware, software, or electronic data.
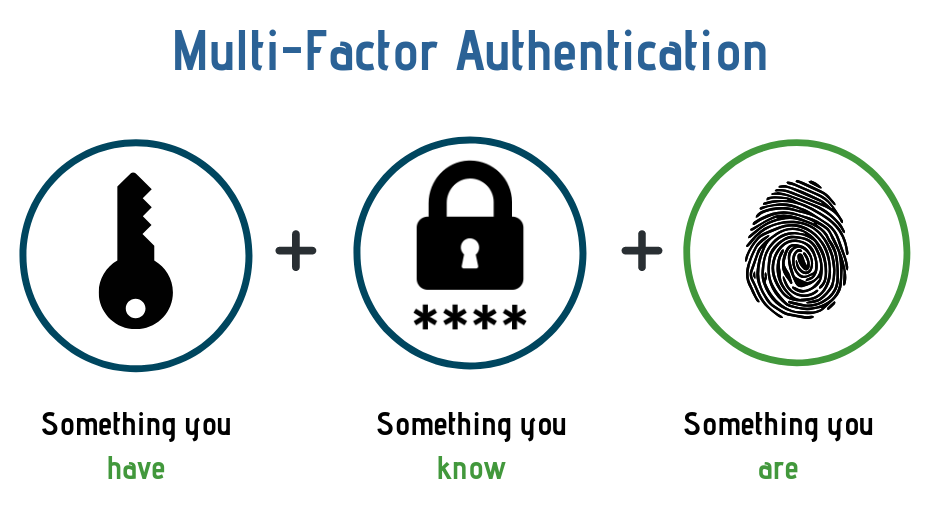
Multi-factor authentication (MFA; encompassing two-factor authentication[2FA], along with similar terms) is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence (or factors) to an authentication mechanism.
The factors used to provide proof of identity include:
- Knowledge Something only the user knows (eg a Password)
- Possession Something only the user has (eg a Credit Card)
- Inherence Something only the user is (eg a Fingerprint)
MFA protects the user from an unknown person trying to access their data such as personal ID details or financial assets.

2 FACTOR AUTHENTICATION
What is 2FA, July 16, 2021
2 Factor Authentication is a subset of MultiFactor Authentication that uses 2 factors to prove the user's identity.
Two-factor authentication can be used to strengthen the security of an online account, a smartphone, or even a door. Before the secured entity is accessed, the user must provide the two required authentication factors.
Authentication takes place when someone tries to log into a computer resource (such as a network, device, or application). Password-protection is the most commonly implemented method of authentication but that has led to malicious hackers to invent multiple attacks to acquire passwords. As a result, passwords alone can no longer be used to implement cybersecurity.
Types of 2FA include:
- Authenticator App / TOTP (Time-based One Time Password) - part of the OATH(Open authentication) architecture and is a phone-based option for 2FA which uses an application that generates codes locally based on a secret key every 30 seconds or so. The user would then enter the code during logging in. Eg Google Authenticator.
- Push-based 2FA - works by sending a prompt to one of the user's devices during login. The prompt indicates the estimated location of the log in attempt and allows the user to approve or deny the attempt. Eg Duo Push and Apple’s Trusted Devices method.
- Security key / FIDO U2F(Universal Second Factor) - a relatively new style of 2FA, typically using small USB, NFC or Bluetooth Low Energy (BTLE) devices often called “security keys”. The U2F device is registered with a site then during logins, the user is prompted to connect the device and tap it to allow the login.
Note: critics argue that text messages are not a true form of 2FA since they are not something the user already has but rather something the user is sent, and the sending process is vulnerable. Instead, the critics argue that this process should be called two-step verification.
Alvyne Wamwea Mwaniki
Other Posts
Tags
2FA 2 Factor Authentication Electronic Authentication Infromation Security Cybersecurity